

The model also became known as the Thomson model, although its chief proponent was William Thomson (Lord Kelvin), not J.J. In Thomson’s analogy, negatively charged corpuscles were like raisins suspended in a positively charged cake, resulting in a neutral atom. This model of the atom became known as the “plum pudding” model, so named for the popular English dessert. Thomson described his experiments with cathode rays to verify the existence of these subatomic corpuscles. “The atoms of the ordinary elements are made up of corpuscles and holes, the holes being predominant,” he continued. Thomson, during a lecture at the Royal Institution in London, on 30 April 1897. He was unsure if the particles were gases, atoms or matter in a finer state of subdivision.“We shall call such particles corpuscles,” announced the physicist J.J. Thomson then went on to extract all gases from the cathode ray tube to try and identify all particles in the experiment. Both cylinders had holes or slits.Īll attempts failed when he tried to use the bent rays. The outer cylinder was grounded while inner was attached to an electrometer to detect any electric current as shown in the figure below. The cylinders were coaxial placed and insulated from each other. The experiment apparatus consisted of two metal cylinders. How does a cathode ray tube experiment work? However, Thomson’s contributions remain more significant than the rest. Thomson was not the only one working on cathode rays, but several other players like Julius Plücker, Johann Wilhelm Hittorf, William Crookes, Philipp Lenard had contributed or were busy studying it.
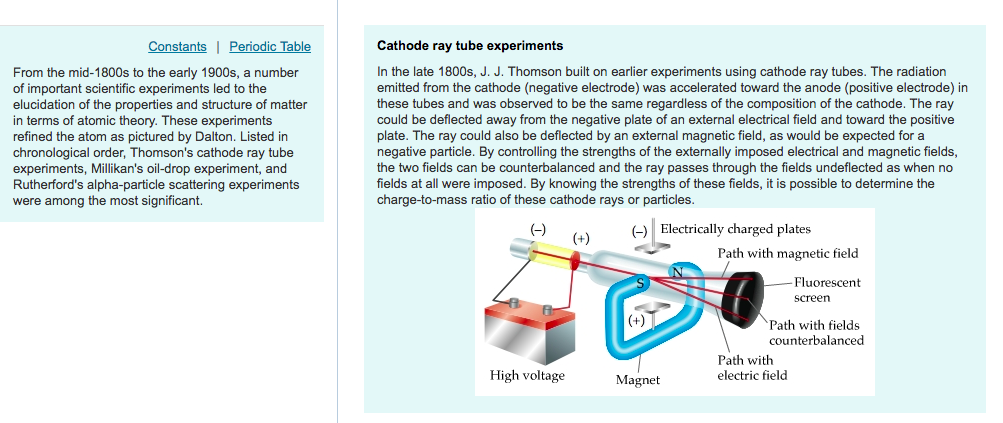
The apparatus of his experiment is called the cathode-ray tube (CRT). Who was the first person to use the cathode ray tube? It is a vacuum sealed tube with a cathode and anode on one side. He did this using a cathode ray tube or CRT. Thomson’s cathode ray experiment was a set of three experiments that assisted in discovering electrons.
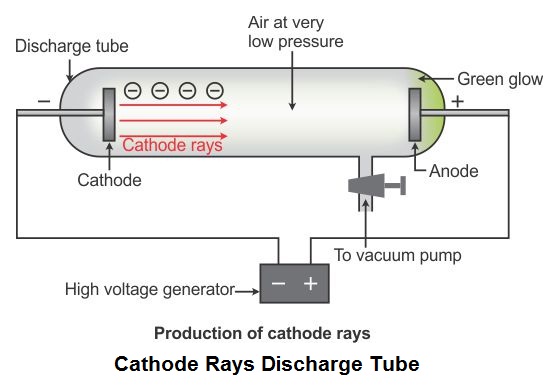
How did j.j.thomson do his cathode ray experiment? In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. Rutherford’s atomic model became known as the nuclear model. What did Rutherford discover and what was his model called? These subatomic particles can be found within atoms of all elements. The particles must exist as part of the atom, since the mass of each particle is only ∼ 20001start fraction, 1, divided by, 2000, end fraction the mass of a hydrogen atom. The cathode ray is composed of negatively-charged particles. Thomson invented to test the theory that negative charges in an atom were real. What is the cathode ray tube? The cathode ray tube was what J.J. Thomson is the scientist that discovered electrons through an experiment called the Cathode Ray Experiment. What was discovered in the cathode ray tube experiment quizlet? In May 1932 James Chadwick announced that the core also contained a new uncharged particle, which he called the neutron. By 1920, physicists knew that most of the mass of the atom was located in a nucleus at its center, and that this central core contained protons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
